Read 180 Universal Assessments for System 44
Nationally, i-third of American heart school students fail to demonstrate competency over course-level reading skills (NAEP, 2017). Students who practise not meet or exceed benchmark scores on state and national tests are less likely to graduate from high school, are less probable to persist in or successfully complete time to come bookish and workplace training endeavors, and are overall less likely to be on track for time to come academic and workplace success (CCRSC, 2013). The Lincoln Unified School District identified the demand for an intervention to accelerate the district's most struggling readers to grade-level reading proficiency.
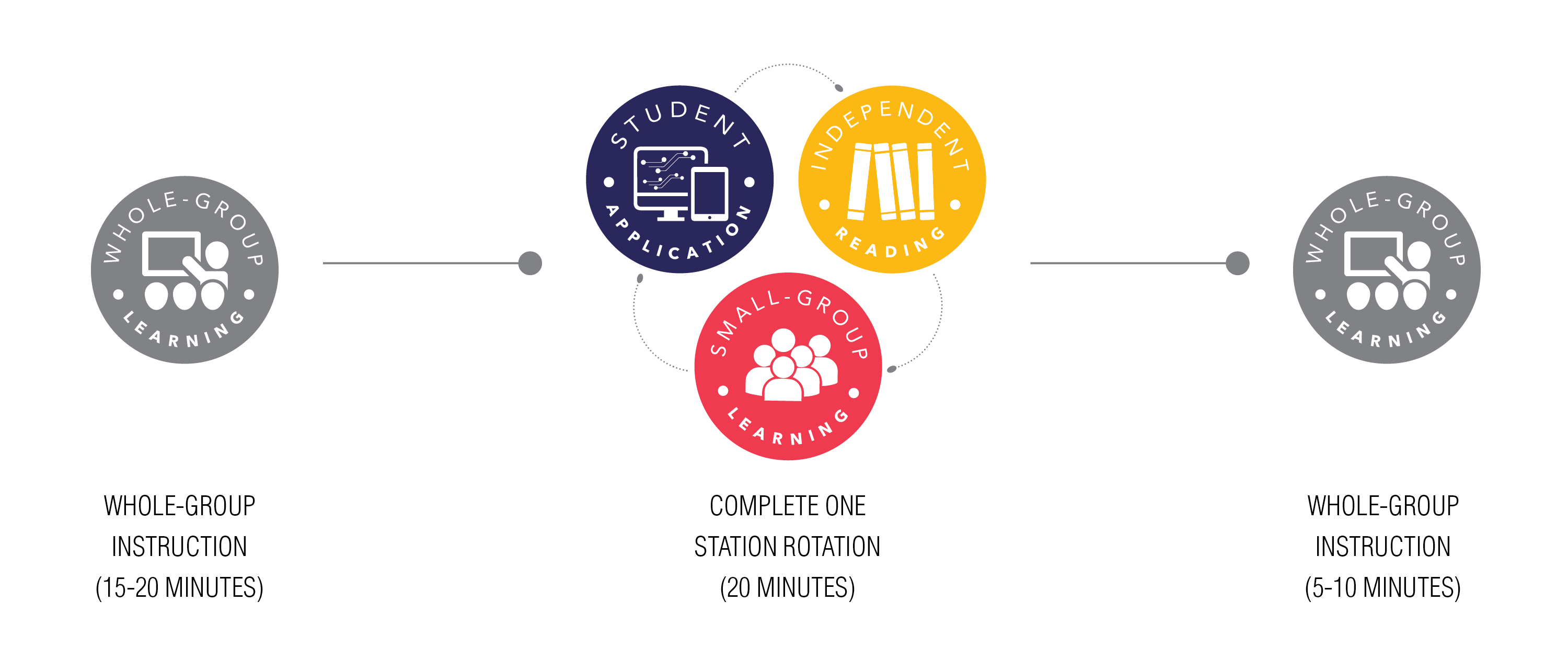
READ 180 Universal is an intervention program designed by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt® to build reading comprehension, academic vocabulary, and writing skills for struggling students in Course 4 and upward. Students progress through six workshops that include differentiated education, adaptive software, writing tasks, contained reading, and projection-based learning assessments. This composite learning solution begins with whole-group learning that focuses on close-reading strategies, academic vocabulary exercises, writing practice, and discussions, then rotates betwixt the following: a) student application with a personalized path of self-paced independent piece of work; b) student-selected independent reading textile to make reading a daily habit; and c) minor groups with data-driven pedagogy, all of which is followed by a whole-grouping wrap-upwards. READ 180 Universal utilizes engaging and relevant content and research-based digital solutions to motivate students and increase reading fluency and comprehension.
System 44 is an intervention program designed to build foundational reading and decoding skills for the most challenged readers. This blended learning solution includes daily reading, writing, talking, and critical thinking exercises. Materials feature modeled and independent reading with age-appropriate books that target decoding skills and strategies to promote comprehension, build vocabulary, and increase content-area noesis. Using adaptive technology, students complete a personalized learning progression through five strands that include The Code, Word Strategies, Sight Words, Success, and Writing. Arrangement 44 is designed to exist used in conjunction with READ 180 Universal in integrated classrooms to serve every bit differentiated instruction during small group and the software rotation.
Students in Grades six, 7, and 8 experienced the Double Period Instructional Model for 90 minutes approximately three days a calendar week.
The Lincoln Unified Schoolhouse Commune (LUSD) in Stockton is one of one,228 school districts in California. LUSD served nine,420 Thousand–12th-grade students in the 2017–2018 school twelvemonth, of which, eight unproblematic schools served 5,630 PreK-8thursday-course students and one middle school served 658 7th–8th-grade students . LUSD serves a diverse population of students with a range of ethnic backgrounds: African American (12%), Asian (13%), Caucasian (22%), Hispanic (48%), Native American (2%), and students with multiple ethnic backgrounds (three%). In the 2017–2018 schoolhouse year, 63% of students in the district were eligible to receive complimentary or reduced-cost luncheon through the National Schoolhouse Tiffin Programme, xv% were classified as English learners (EL), and xi% were classified every bit Students with Disabilities (SWD).
All schools serving 6th–viiith-grade students in LUSD utilized READ 180 Universal as a Tier 2 reading intervention and System 44 every bit a Tier 3 reading intervention during the 2017–2018 school year in integrated classrooms with differentiated instruction. All students who completed at to the lowest degree xv READ 180 Universal sessions totaling at to the lowest degree 150 minutes and no System 44 sessions (north = 251) or who completed at to the lowest degree 10 sessions each in both System 44 and READ 180 Universal totaling at least 150 minutes (n = 38) were included in the analysis; 41 students with less use were excluded from this analysis. Students in this analysis attended Brookside School (northward = xx), Claudia Landeen Schoolhouse (n = 27), Colonial Heights School (northward = 26), Don Riggio School (due north = 41), John R Williams School (n = twenty), Lincoln Elementary School (due north = xix), Mable Barron School (n = 26), Tully C Knoles School (n = 32), and Sierra Middle School (northward = 78). Student ethnic backgrounds included African American (19%), Asian (8%), Caucasian (13%), Hispanic (55%), and Native American (2%), and students with multiple ethnic backgrounds (3%). Of these students, 60% were male and 40% were female person, 84% were eligible to receive costless or reduced-cost tiffin through the National School Dejeuner Program, 34% were classified as EL, and 31% were classified every bit students with disabilities.
LUSD students in Grades vi to 8 were identified as struggling with reading comprehension based on a blueprint of below grade level Measures of Bookish Progress (MAP®) scores, DIBELS®, Smarter Balanced Cess English Language Arts/Literacy scores and Reading Inventory Lexile® scores. Students who scored less than 600 Lexile (L) measures on the Reading Inventory completed the Phonics Inventory; those students who scored in the "Get-go" or "Developing" range worked in System 44 until moving to READ 180 Universal afterward scoring in the "Advancing" range (chosen mixed-model implementation hereafter). Those students who scored in the recommended Lexile (Fifty) range on the Reading Inventory (between 600-880L in Course six, 600-950L in Grade vii or 600-990L in Grade 8 ) began READ 180 Universal teaching.
Students in Grades 6, 7, and 8 received 90-minute Arrangement 44 and/or READ 180 Universal didactics approximately three times a week. In this Double Period Educational activity Model, students completed 20 minutes of whole-group didactics followed by 20 minutes of each of three station rotations (rotated betwixt the personalized online pupil application in either System 44 or READ 180 Universal, differentiated small-group learning, and contained reading), and concluding with 10 minutes of whole-group wrap-upwardly.
LUSD teachers completed a ii-mean solar day "Getting Started" training to learn how to use the Arrangement 44 and READ 180 Universal plan technology, differentiation features, and plan assessments in the 2016–2017 school year (the first twelvemonth of implementation). Teachers also had 29 coaching days in the 2017–2018 school year and 12 days of coaching in the 2017–2018 school year to learn about effective planning, progress monitoring, and to receive further education on using differentiation and assessments.
Student software usage data was nerveless equally students used the online educatee application during Arrangement 44 and READ 180 Universal instruction. Software usage data included number of completed segments, number of completed sessions, boilerplate time spent in each session, and number of sessions averaged per calendar week.
The Smarter Balanced Assessment (SBA) was designed to mensurate end-of-year achievement in English Language Arts/Literacy (ELA) and to accurately capture growth in ELA proficiency from previous years. The SBA measures ELA achievement in reading, writing, listening, and research using a computer adaptive system to deliver between 42 and 48 questions. Assessment results include a scale score between 2,000 and 3,000 and an achievement level descriptor (ALD) indicating overall operation level of Standard Not Met, Standard Nearly Met, Standard Met (indicating grade-level ELA proficiency), and Standard Exceeded. LUSD students complete the SBA each bound in Grades three–8 and also in Class eleven. SBA scores are a part of the California Assessment of Educatee Performance and Progress (CAASPP).
The Reading Inventory measures reading comprehension proficiency for students in Grades K–12. The Reading Inventory uses adaptive technology to determine a student's reading comprehension level on the Lexile Framework for Reading; the higher the Lexile score, the more challenging reading material the student can comprehend. Test particular difficulty ranges from items advisable for developing readers to items requiring a reading proficiency indicating preparedness for college-level texts, allowing measurement of skill growth regardless of the students' initial ability. Assessment results include a Lexile scale score that indicates reading ability at a level of text complication and a performance level of below basic, basic, skilful, or advanced, indicating accomplished reading comprehension compared to grade-level expectations. LUSD students receiving Arrangement 44 and READ 180 Universal didactics completed the Reading Inventory in the fall of 2017 (August through Oct) before beginning pedagogy, once more in the winter (Nov through January), and again in the jump of 2018 (Apr or May) post-obit instruction.
The HMH Phonics Inventory measures proficiency in the foundational reading skills of phonological decoding and sight word reading for students in Grades 3–12. The Phonics Inventory is used to identify whether students with low reading comprehension accomplishment also lack the skills needed to decode new words (leading to placement in System 44) or are best served by an intervention to develop reading comprehension strategies, text assay skills, and groundwork knowledge (leading to placement in READ 180 Universal). Cess results include a fluency score and decoder status of pre-decoder, beginning, developing, or advancing. LUSD students with Reading Inventory scores at 400L or below completed the Phonics Inventory earlier outset instruction in System 44, and every couple of months following education until promotion to READ 180 Universal.
LUSD students whose home linguistic communication is not English and students who are classified every bit English learners complete an English linguistic communication proficiency test each bound. For the 2016–2017 school year, students completed The California English Language Evolution Test (CELDT). The CELDT was designed to identify students who demand to improve their skills in listening, speaking, reading, and writing in English. Students are assessed on the five domains of Reading, Writing, Listening, Speaking, and Comprehension. Cess results include a scale score for each domain as well as an overall scale score with a range from 248–741 in Grades vi–viii. For the 2017–2018 schoolhouse year, the summative English Language Proficiency Assessments for California (ELPAC) replaced the CELDT to measure an English learner's progress in learning English language and to identify the student'southward English language proficiency level. Assessment results include a scale score for each category of Oral Language (Listening, Speaking) and Written Language (Reading, Writing), an overall scale score with a range from one,150 to 1,900, and an overall performance level from 1 to 4 (outset English to well-developed English language skills). The ELPAC, based on new California English Development Standards, does non produce scores that are comparable to CELDT scores.
Every bit LUSD uses frequent cess data to place students into the appropriate tier of reading intervention when needed and leave students afterwards reaching the appropriate level of proficiency, LUSD students may participate in an intervention for just one or both semesters of a school year and then motion into some other intervention or to standard instruction. Students who received READ 180 Universal teaching for the entire school year completed an boilerplate of 6.9 segments (SD = 4.81) over an average of 77.ane full sessions (SD = 25.45), with ii.viii (SD = 0.58) sessions averaged a week in the READ 180 Universal online student application. Each session lasted an boilerplate of 15.08 (SD = 3.72) minutes. These metrics are consequent with the implementation model. Students who completed at least 10 sessions each of both System 44 and READ 180 Universal teaching during at least 150 session minutes (in the mixed model implementation) during the 2017-2018 school yr completed an average of four.3 READ 180 Universal segments (SD = three.64) over an average of 42.5 total sessions (SD = xx.64), with 2.7 (SD = 0.52) sessions averaged a week and averaging 15.4 minutes (SD = 3.71) per session in the READ 180 Universal online student awarding. Students in this mixed model implementation also completed an average of 26.six System 44 topics (SD = 15.51) over an boilerplate of 39.0 full sessions (SD = 25.74), averaging 11.1 minutes (SD = 2.27) per session in the System 44 online student application.
An independent evaluator from Forge Research Group analyzed student academic accomplishment using test score data provided by the Lincoln Unified School Commune and program usage data provided past Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. READ 180 Universal and System 44 + READ 180 Universal mixed-model students' ELA performance was examined pre- and post-implementation using multiple independent measures of reading. This analysis included scores on the statewide end-of-yr summative assessment (SBA), the Reading Inventory, and the Phonics Inventory. READ 180 Universal students and the mixed model students demonstrated statistically significant gains in ELA proficiency during the 2017–2018 school year on each of these reading measures.
LUSD students took the SBA ELA summative cess in bound 2017, prior to receiving READ 180 Universal, and again in spring 2018, after instruction. READ 180 Universal students demonstrated a statistically significant overall gain in SBA ELA scale score, averaging a 39-point increase from 2,426 in 2017 to 2,465 in 2018 (run across Figure one). Farther, the increase in the average the SBA ELA calibration score was statistically meaning for Grade six (56-point gain), Grade seven (41-point gain) and Grde 8 (21-point gain) students. Mixed-model students also demonstrated a statistically significant overall proceeds in SBA ELA scale score, averaging a 49-point increment from 2,413 in 2017 to 2,462 in 2018. Notably, mixed-model students decreased the scale score gap from 13 points to 3 points, ending the year at a similar SBA scale score equally compared to the READ 180 Universal students.

FIGURE 1. Change in Smarter Balanced Assessment English Linguistic communication Arts Scale Scores Overall, by Program and past Grade, 2017–2018
Note. * = statistically significant change. The increase in the average SBA ELA scale score was statistically pregnant for READ 180 Universal students overall (t = x.41, p = 0.00) and for Grade 6 (t = 8.10, p = 0.00), Grade 7 (t = 7.54, p = 0.00), and Grade 8 (t = 3.24, p = 0.00). The increment in the average SBA ELA scale score was statistically meaning for mixed-model (System 44 + READ 180 Universal) students overall (t = 5.40, p = 0.00).
Notably, students showed accelerated growth in SBA ELA percentile compared to their initially same-scoring peers – on average, students scored better than 18% of their peers in 2017 just meliorate than 21% of their peers in 2018, a statistically significant increase.
READ 180 Universal students who completed the Reading Inventory in both the fall of 2017 and the spring of 2018 demonstrated a statistically significant overall gain in Lexile scores, averaging a 119L increment from 613L in fall to 732L in spring (see Figure two). Farther, the increase in average Reading Inventory scores was statistically significant for Grade 6 (137L gain), Grade seven (110L gain), and Grade 8 (112L gain) students. Mixed model students also demonstrated a statistically pregnant overall proceeds in Lexile scores, averaging a 244L increase from 428L in fall to 672L in jump. Notably, mixed-model students started the school twelvemonth at a lower form-level power of reading comprehension simply decreased the Lexile score gap from 185L to 60L, ending the year in the same form-level Lexile range equally the READ 180 Universal students.

Effigy two. Change in Reading Inventory in Lexile Score Overall, past Plan and by Grade, Fall 2017 to Leap 2018
Notation. * = statistically significant alter. The increase in the average Reading Inventory Lexile score was statistically significant for READ 180 Universal students overall (t = 13.25, p = 0.00) and for Class half-dozen (t = vi.40, p = 0.00), Grade 7 (t = 8.99, p = 0.00), and Class viii (t = 8.87, p = 0.00). The increase in the average Reading Inventory Lexile score was statistically significant for mixed-model students overall (t = 8.lxxx, p = 0.00).
In addition to demonstrating statistically significant Lexile gains, READ 180 Universal and the mixed-model students demonstrated accelerated Lexile score gains compared to the average almanac growth demonstrated by an initially same-scoring national sample . Notably, on average, students gained approximately 1.iv times as many Lexile scores as would be expected from beginning to exiting teaching (run into Figure iii), demonstrating accelerated growth towards grade-level performance.

FIGURE iii. READ 180 Universal Students' Lexile Score Gains Compared to the Expected Lexile Gain Based on a National Sample, Fall 2017 to Spring 2018
Note. * = statistically significant change. The boilerplate Reading Inventory Lexile score gain was statistically significantly greater than the expected Lexile score gain for READ 180 Universal students overall (t = three.21, p = 0.00) and for Grade vi (t = 2.42, p = 0.02) and Form seven (t = 2.82, p = 0.01). The increment in the boilerplate Reading Inventory Lexile score was statistically significant for mixed-model (System 44 + READ 180 Universal) students overall (t = iv.31, p = 0.00).
Summary Growth Metrics (see Figures 4 and five) show the significant extent of reading comprehension growth during the 2017-2018 schoolhouse year. With just ane year of use, the majority of READ 180 Universal students accomplished a Lexile gain on Reading Inventory (87%) and met finish-of-yr growth expectations (60%) based on Estimated Average Annual Growth4 adjusted for the number of days in the program. Additionally, thirty% of READ 180 Universal students more than doubled end-of-year growth expectations, and 31% of students increased at least one level on Reading Inventory College & Career Operation Levels.
Demonstrating accelerated growth, most all mixed-model students achieved a Lexile gain on the Reading Inventory (97%) and a large bulk met finish-of-year growth expectations (74%) based on Estimated Boilerplate Almanac Growth adjusted for the number of days in the plan. Additionally, 53% of mixed-model students more doubled end-of-year growth expectations, and 41% of students increased at to the lowest degree ane level on theReading Inventory College & Career performance levels.

FIGURE 4. READ 180 Universal Students (North = 247) Summary Growth Metrics
Note. EOY = End-of-twelvemonth; 2X = ii times; CCR = College and Career Readiness.

Effigy 5. Integrated Instruction Students (N = 38) Summary Growth Metrics
Note. EOY = Finish-of-twelvemonth; 2X = two times; CCR = Higher and Career Readiness.
Chiefly, READ 180 Universal students increased in class-level reading ability (based on the text complexity class correlated with the Lexile range aligned to college and career readiness) during the 2017-2018 schoolhouse year (see Figure six). The pct of Grade vi, Form 7, and Grade viii students who demonstrated at to the lowest degree form-level reading comprehension increased 6-fold from 1% to half-dozen% and the percentage who demonstrated reading comprehension power v or more than grades below form level decreased from 42% to 22%. With just one twelvemonth of education, 27% of the students increased 2 or more class levels in reading comprehension.
Too, mixed-model students increased in form-level reading power during the 2017-2018 school yr (run across Figure seven). The pct of Grade 6, Grade 7, and Grade 8 students who demonstrated at least course-level reading comprehension increased from 0% to 3% and the percentage who demonstrated reading comprehension ability five or more grades below course level decreased from 60% to 21%. With but i year of pedagogy, xv% of the students increased two or more than grade levels in reading comprehension. On boilerplate, mixed-model students began the year demonstrating reading comprehension skills five grades below class-level and averaged reading comprehension skills three grades below grade-level by the finish of the year. Of note, increasing a course level at the lower simple school reading comprehension level requires close to twice as many Lexile score gains as does an increase in grade level power at the middle school level. As such, the increase of one grade level in reading comprehension represents more absolute growth for the students with the lowest initial form-level reading power than for students with the highest initial class-level reading ability.
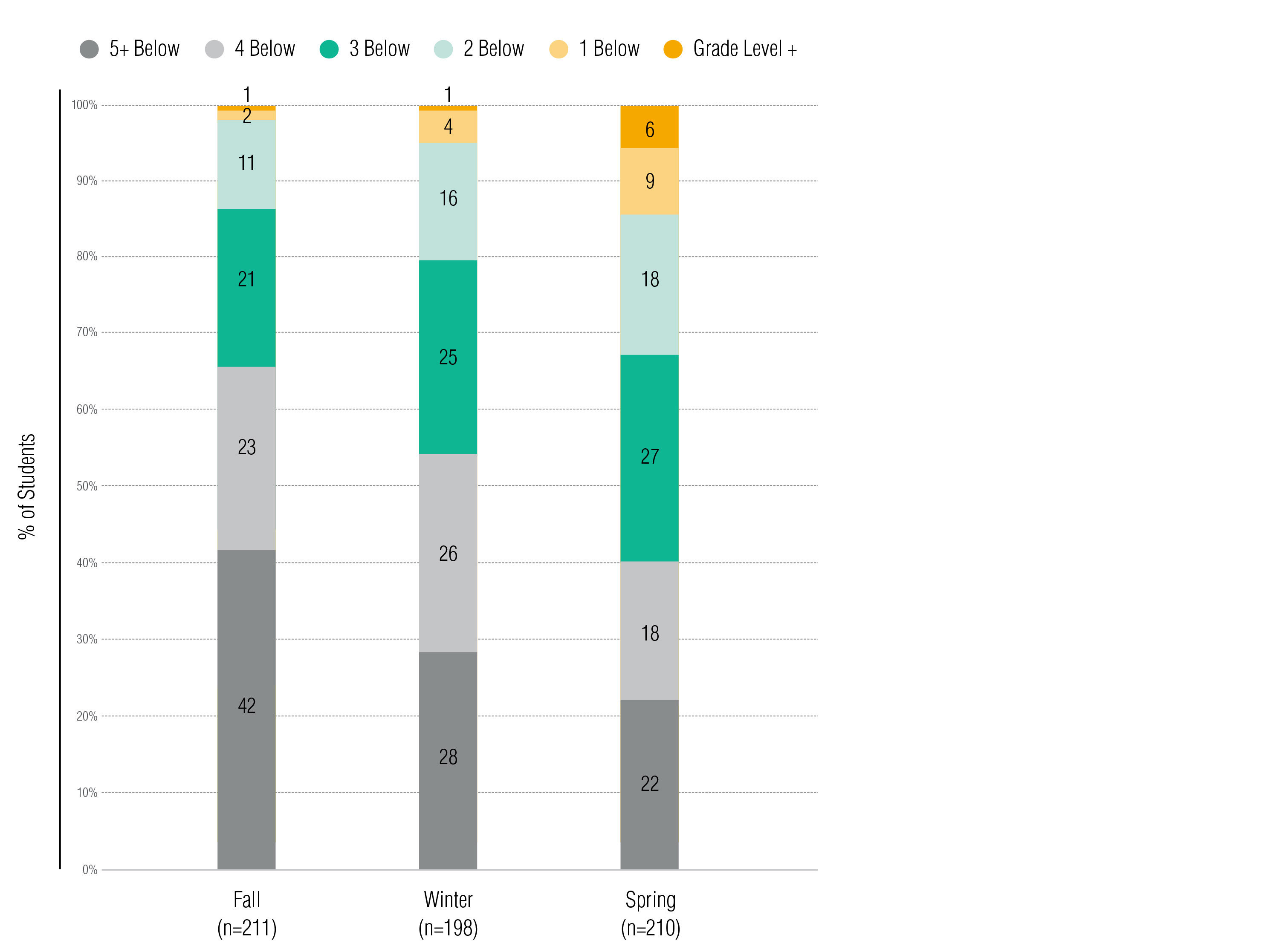
Effigy 6. READ 180 Universal Students' Change in Class-Level Reading Ability in Equivalent Lexile Scores, 2017–2018
Note. The READ 180 Universal students' increase in class-level reading ability was statistically significant from fall to spring (t = 12.29, p = 0.00), autumn to wintertime (t = seven.48, p = 0.03), and winter to leap (t = 7.76, p = 0.00).

Effigy 7. Mixed-Model Students' Change in Grade-Level Reading Power in Equivalent Lexile Scores, 2017–2018
Notation. The mixed-model students' increment in grade-level reading ability was statistically pregnant from fall to spring (t = 6.67, p = 0.00), autumn to winter (t = 4.fifteen, p = 0.03), and wintertime to jump (t = 5.18, p = 0.00).
Notably, growth on the Reading Inventory from fall 2017 to bound 2018 was highest for the most struggling readers. READ 180 Universal Didactics students who initially scored in the Below Basic performance level on the Reading Inventory gained an average of 133L (large outcome size of Cohen's d = .86) during the 2017-2018 schoolhouse twelvemonth, demonstrating accelerated growth in approaching grade-level proficiency compared to students who initially scored in the Basic performance level, who gained an average of 57L (medium-large effect size of Cohen's d = .75). All mixed-model students initially scored in the Below Basic performance level, but gained an average of 244L during the 2017-2018 school year (large upshot size of Cohen's d = 1.61).
Further, increased employ of the READ 180 Universal online software was a statistically significant predictor of reading Lexile score growth, both before and subsequently correcting for option bias (see Appendix Table 6 for details). On average, READ 180 Universal students who completed more segments of the READ 180 Universal online software likewise achieved college gains in the Reading Inventory Lexile score (see Effigy 8). Students who completed ten or more than segments of the online software achieved an boilerplate of 1.5 times more Lexile score gain (143L) compared to students who completed ane to 3 segments (98L). Similarly, for mixed-model students, as the number of Organization 44 topics completed increased and so did pupil Lexile score gain on the Reading Inventory; this positive correlation was too statistically meaning.

FIGURE 8. READ 180 Universal Students' Average Gain on Reading Inventory in Lexile Score by Implementation Level, Autumn 2017 to Spring 2018
Note. Reading Inventory Lexile score gains increased between completing minimal (1-three segments), depression (4-vi segments), moderate (7-9 segments), and loftier (ten or more than segments) levels of implementation. Number of READ 180 Universal segments completed was a pregnant predictor of Reading Inventory Lexile score subsequently accounting for initialReading Inventory Lexile score (B = 3.85, F = 10.55, p = 0.01, Adjusted R2 = .25).
Mixed-model students besides demonstrated statistically significant gains in Phonics Inventory fluency scores (see Figure nine), increasing from an boilerplate of 12 on kickoff assessment to 18 on the final assessment. The percent of students achieving an "Advanced" decoder condition increased from 0% to 33%, while the percent of students scoring at a "Developing" decoder status decreased from 50% to 21% from 2017 to 2018 (run across Figure 10).

FIGURE ix. Mixed Model Students' Alter in Phonics Inventory Fluency Score Autumn 2017 to Leap 2018
Annotation. * = statistically meaning change. The increase in HMH Phonics Inventory fluency score was statistically significant (t = iv.twoscore, p = 0.00).

FIGURE x. Mixed-Model Students' Alter in Phonics Inventory Decoder Status, Fall 2017 to Spring 2018
Note. * = statistically significant change. The increase in HMH Phonics Inventory Decoder Condition was statistically significant (t = 4.i, p = 0.00).
In add-on to SBA scale score and Reading Inventory Lexile gains, READ 180 Universal students besides achieved increased performance levels on reading measures (run across Figures 11 and 12). The percent of students achieving a "Standard Met" SBA ELA Achievement Level Descriptor (ALD) increased from 0% to 7%, while the percent of students scoring at a "Standard Not Met" ALD decreased from 79% to 55% from 2017 to 2018. The percent of students achieving at to the lowest degree a Skilful Reading Inventory functioning level increased six-fold from 1% to 6% and the percent of students scoring at a Beneath Basic performance level decreased from 76% to 50% from 2017 to 2018. The increase in students' operation levels on both the SBA ELA assessment and the Reading Inventory was statistically pregnant.

FIGURE 11. READ 180 Universal Students' Change in Smarter Balanced Assessment (SBA) English language Linguistic communication Arts (ELA) Accomplishment Levels, 2017–2018
Notation. The increase in SBA ELA Achievement Level Descriptor was statistically significant (t = six.96, p = 0.00).
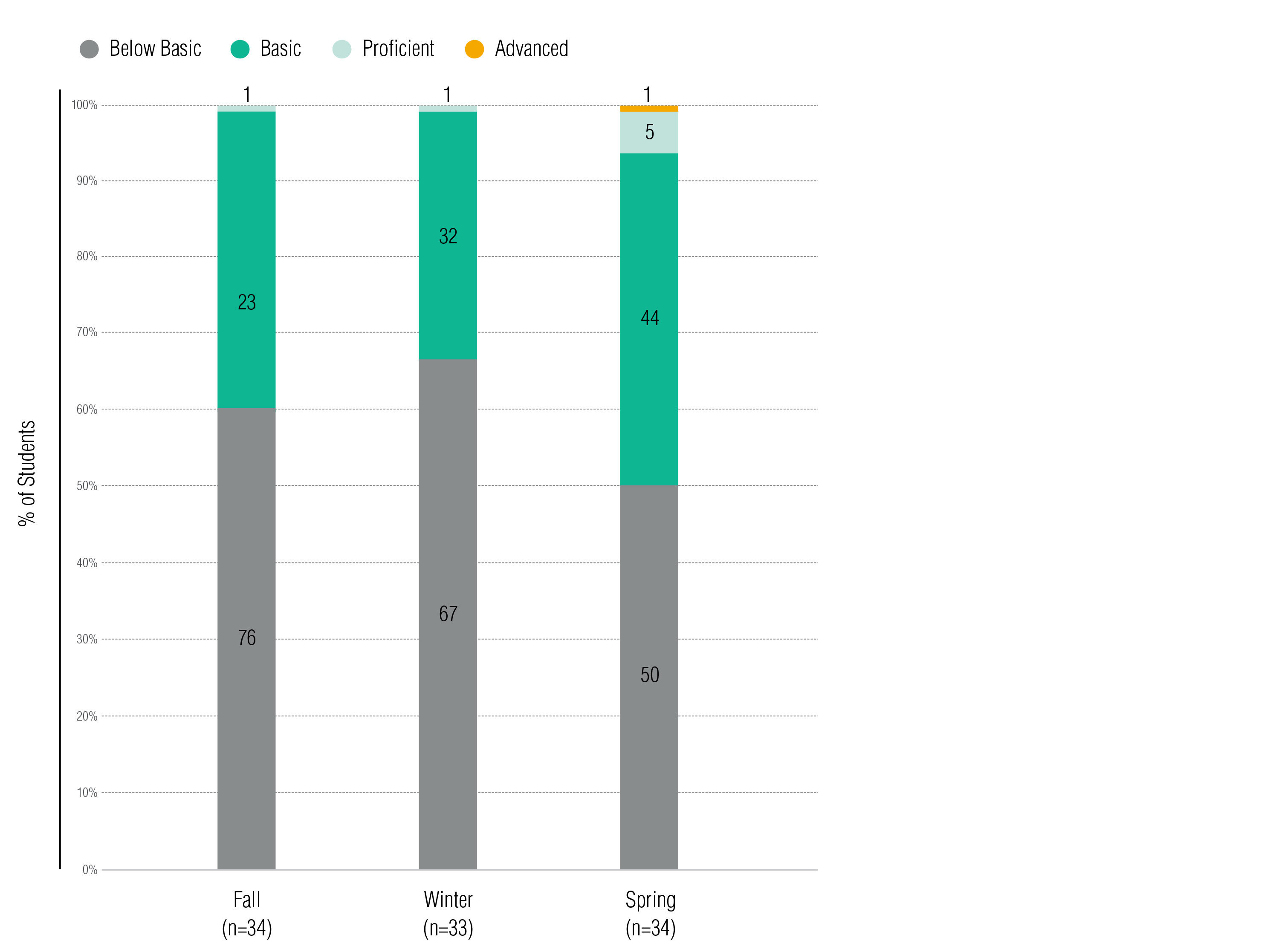
Figure 12. READ 180 Universal Students' Change in Reading Inventory Functioning Levels, Autumn 2017 to Spring 2018
Note. The increase in Reading Inventory Performance Level was statistically pregnant (t = 9.02, p = 0.00).
Mixed-model students as well achieved increased operation levels on reading measures (come across Figures 13 and 14). The percent of students achieving at a "Standard Nearly Met" SBA ELA Achievement Level Descriptor (ALD) increased from 3% to 55% while the per centum of students scoring at a "Standard Not Met" ALD decreased from about everyone at 94% to less than one-half at 42% from 2017 to 2018. The percent of students achieving at least a Proficient Reading Inventory performance level increased from 0% to iii% and the percent of students scoring at a Below Basic performance level decreased from 100% to 59% from 2017 to 2018. The increase in students' performance levels on both the SBA ELA assessment and theReading Inventory was statistically significant.

Effigy 13. Mixed-Model Students' Alter in Smarter Counterbalanced Cess (SBA) English language Linguistic communication Arts (ELA) Achievement Levels, 2017–2018
Note. The increase in SBA ELA Achievement Level Descriptor was statistically significant (t = four.78, p = 0.00).

Effigy xiv. Mixed-Model Students' Change in Reading Inventory Performance Levels, Fall 2017 to Spring 2018
Note. The increase in Reading Inventory Functioning Level was statistically significant (t = 4.59, p = 0.00).
After one year of READ 180 Universal instruction or mixed-model educational activity, many students increased an achievement level descriptor on the state summative cess (33% and fifty%, respectively), and/or increased a functioning level on theReading Inventory (31% and 41%, respectively).
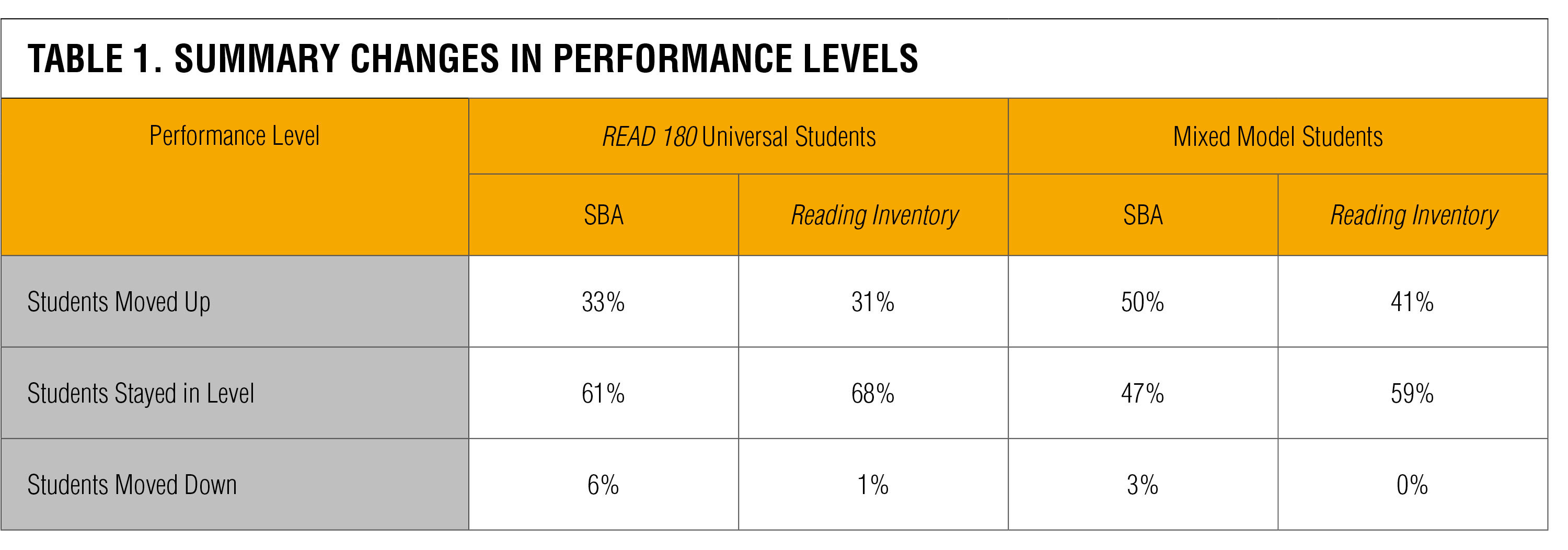
Annotation. SBA = Smarter Counterbalanced Cess Summative English Language Arts/Literacy
Notably, disaggregation of the information indicated that use of both READ 180 Universal lonely or in a mixed-model implementation with System 44 was associated with significant gains in both SBA ELA scale scores and Reading Inventory Lexile gains for all categories of students (results are presented together here but see Appendix for a separation by pedagogy grouping).
When results were disaggregated by gender, both males and females achieved statistically pregnant SBA ELA scale score gains (see Figure 15) and Reading Inventory gains (run across Figure 16) from pre- to post-instruction.

FIGURE 15. Alter in Smarter Balanced Assessment English Language Arts Scale Score by Gender, 2017–2018
Notation. * = statistically significant modify. The increment in boilerplate SBA ELA calibration score was statistically significant for male person (t = 7.84, p = 0.00) and female (t = 10.43, p = 0.00) students.

Effigy xvi. Alter in Reading Inventory in Lexile Score by Gender, Fall 2017 to Spring 2018
Note. * = statistically significant alter. The increase in average Reading Inventory Lexile score was statistically pregnant for male (t = 11.50, p = 0.00) and female person (t = 9.49, p = 0.00) students.
When results were disaggregated by education classification, students with disabilities achieved statistically significant SBA ELA scale score gains (see Figure 17) and statistically significant Reading Inventory gains (see Figure 18). In add-on to gaining an average of 120L on theReading Inventory, 51% of the SWD met yearly growth expectations.

Effigy 17. Modify in Smarter Balanced Cess (SBA) English Language Arts (ELA) Scale Score past Students with Disabilities Classification, 2017–2018
Note. * = statistically meaning modify. The increment in average SBA ELA scale score was statistically significant for Students with Disabilities (t = v.08, p = 0.00) and was statistically significant for Non Classified (t = xi.72, p = 0.00) students.

FIGURE xviii. Change in Reading Inventory in Lexile Score by Students with Disabilities Classification, Autumn 2017 to Bound 2018
Note. * = statistically significant change. The increase in average Reading Inventory Lexile score was statistically pregnant for Students with Disabilities (t = seven.11, p = 0.00) and Not Classified (t = xiii.xiii, p = 0.00) students.
When results were disaggregated by eligibility to receive gratis or reduced-toll lunch (FRPL) through the National School Tiffin Program, FRPL-eligible students achieved statistically meaning SBA ELA scale score gains (encounter Figure 19) and statistically significant Reading Inventory gains (see Figure twenty). In addition to gaining an average of 129L on theReading Inventory, 62% of the FRPL-eligible students met yearly growth expectations.

Effigy 19. Change in Smarter Balanced Assessment English Language Arts Scale Score by Free or Reduced-Cost Luncheon Eligibility, 2017–2018
Note. * = statistically pregnant modify. The increase in average SBA ELA scale score was statistically significant for FRPL Eligible Students (t = 11.51, p = 0.00) and Students Non FRPL Eligible (t = four.77, p = 0.00).

Figure 20. Alter in Reading Inventory in Lexile Score by Gratis or Reduced-Price Lunch Eligibility, Fall 2017 to Spring 2018
Note. * = statistically pregnant change. The increase in average Reading Inventory Lexile Score was statistically pregnant for FRPL Eligible Students (t = thirteen.45, p = 0.00) and Students Not FRPL Eligible (t = 6.23, p = 0.00).
When results were disaggregated by ethnicity, African American, Asian, Caucasian, and Hispanic students achieved statistically meaning SBA ELA scale score gains (see Effigy 21) and Reading Inventory gains (see Figure 22) during the 2017–2018 school year. Although the sample was too small to capture the true significance of gains statistically, Native American students gained an average of 80L on theReading Inventory and 67% met yearly growth goals.

Effigy 21. Change in Smarter Balanced Cess English Linguistic communication Arts Scale Score by Ethnicity, 2017–2018
Note. * = statistically significant change. The increase in average SBA ELA scale score was statistically significant for African American (t = 5.91, p = 0.00), Asian (t = 4.07, p = 0.00), Caucasian (t = 2.93, p = 0.01), and Hispanic (t = 9.87, p = 0.00) students.
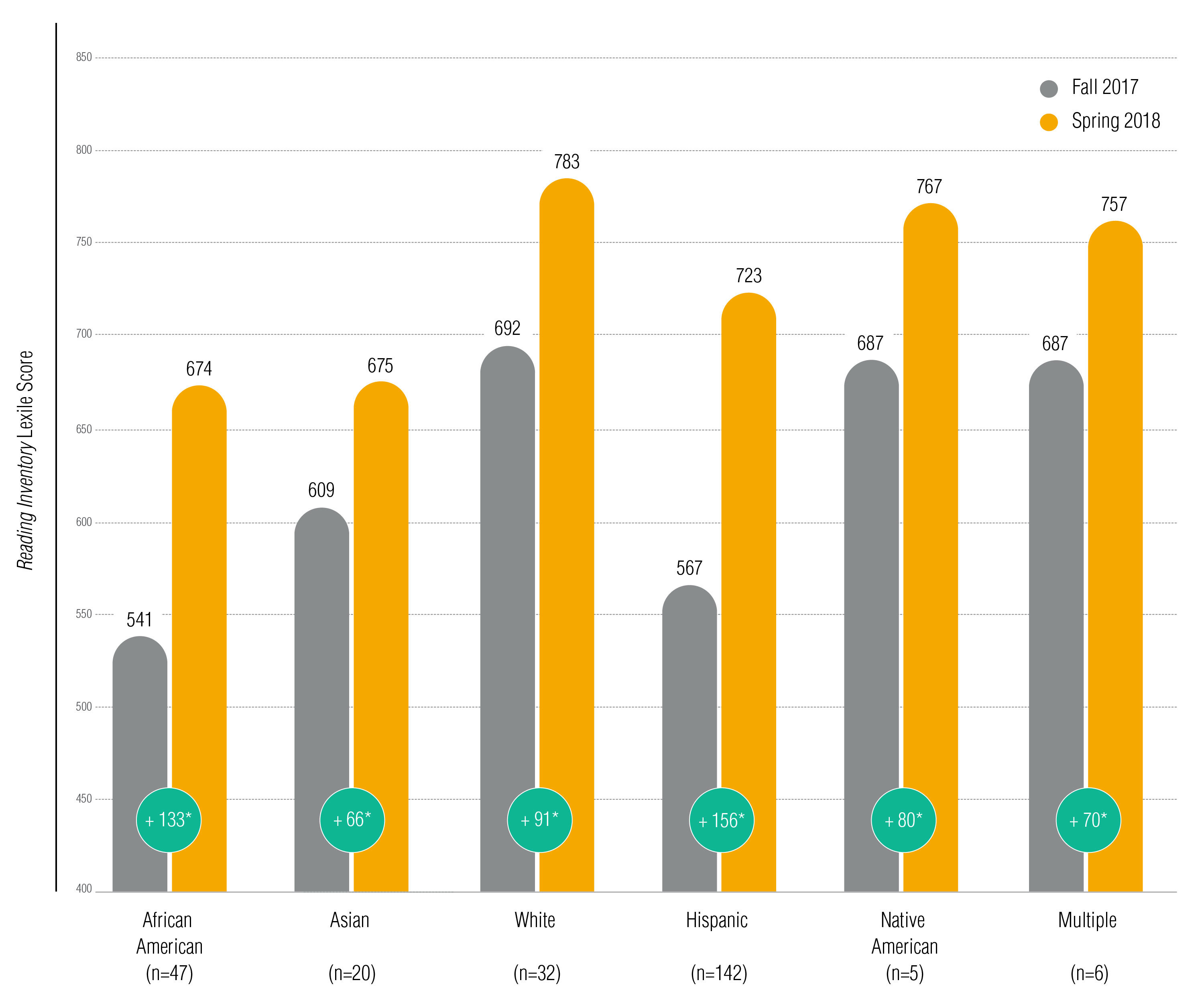
Effigy 22. Change in Reading Inventory in Lexile Score by Ethnicity, Fall 2017 to Spring 2018
Note. * = statistically meaning change. The increase in boilerplate Reading Inventory Lexile Score was statistically meaning for African American (t = 6.61, p = 00), Asian (t = 2.99, p = 0.01), Caucasian (t = 2.84, p = 0.01), and Hispanic (t = thirteen.45, p = 0.00) students and students with Multiple ethnic backgrounds (t = 3.00, p = 0.03).
When results were disaggregated by EL classification, EL students achieved statistically significant SBA ELA scale score gains (meet Figure 23) and meaning Reading Inventory gains (see Figure 24). In addition to an boilerplate gain of 146L on theReading Inventory, 63% of EL students met yearly growth goals.

FIGURE 23. Change in Smarter Balanced Assessment English Language Arts Scale Score by EL Nomenclature, 2017–2018
Note. * = statistically pregnant change. The increase in average SBA ELA scale score was statistically significant for ELs (t = seven.93, p = 0.00) and Not Classified every bit EL (t = ix.65, p = 0.00) students.

Figure 24. Change in Reading Inventory in Lexile Score by EL Classification, Fall 2017 to Bound 2018
Note. * = statistically pregnant alter. The increase in average Lexile scores was statistically significant for English learner (t = 9.73, p = 0.00) and Not Classified (t = 11.29, p = 0.00) students.
LUSD students classified as ELs as well as some students who exited the EL plan in the previous iv years (north = 96) completed the CELDT in spring 2017 and the ELPAC in spring 2018 to measure English proficiency. The CELDT assessment results include an overall scale score with a range from 248 to 741 while the ELPAC results include an overall calibration score with a range from 1150 to 1900. To examine year-to-year changes in scores that are on different scales, the CELDT and ELPAC scores were placed on a mutual calibration using the percent of maximum possible (POMP) calculation . READ 180 Universal and mixed-model EL students averaged a statistically significant 6-point subtract in relative magnitude of scores when comparison 2017 CELDT scores to 2018 ELPAC scores. Equally these assessments measure different skills and define proficiency in unlike ways, it is unclear whether a modify in relative magnitude of scores from 2017 to 2018 reflects a true alter in English language arts skills or is a consequence of a more hard exam, a new examination format, or another unmeasured variable.
Multiple independent measures support the thought that students who received System 44 and/or READ 180 Universal teaching in a mixed-model classroom made significant improvements in English Linguistic communication Arts and Literacy achievement. After one year of instruction, Course 6, seven, and eight students in the Lincoln Unified Schoolhouse Commune demonstrated statistically significant increases in Smarter Balanced Assessment ELA calibration scores, Reading Inventory Lexile scores, and Phonics Inventory fluency scores. In add-on to statistically significant twelvemonth-to-year gains, students achieved accelerated growth in SBA ELA calibration scores compared to initially same-scoring peers and gained approximately 1.4 times as many Lexile scores as would be expected based on the average yearly growth of an initially same-scoring national sample. Overall, the percentage of students demonstrating grade-level or above reading comprehension increased from 1% to half-dozen% afterward one year of instruction, and the percentage of students demonstrating reading comprehension five or more than grades below grade-level decreased from 45% to 22%.
Additionally, 27% of READ 180 Universal pedagogy students and 15% of mixed-model students increased at least two class levels in reading comprehension. Students also increased in assessment functioning levels: 33% of READ 180 Universal instruction students and 50% of mixed-model students moved upwards an Achievement Level Descriptor on the SBA and 31% of READ 180 Universal educational activity students and 41% of mixed-model students moved up a functioning level on theReading Inventory. Notably, on average, Tier 3 intervention students who received a combination of System 44 and READ 180 Universal instruction began the school year with significantly lower SBA ELA scale scores, HMH Reading Inventory Lexile scores, and grade-level reading comprehension ability than the Tier 2 intervention classmates who received READ 180 Universal pedagogy, only demonstrated accelerated learning and averaged gains corking plenty to cease the year at like achievement levels. Disaggregation of the data by gender, SWD status, FRPL eligibility, ethnicity, and EL nomenclature indicated that use of both READ 180 Universal alone or in a mixed model implementation with System 44 was associated with significant gains in both SBA ELA calibration scores and Reading Inventory Lexile gains for all categories of students. Students worked through varying amounts of the self-paced, personalized online pedagogy components – increased completion of System 44 topics was significantly correlated with reading Lexile gains and increased completion of READ 180 Universal segments was a significant predictor of reading Lexile gains during the 2017–2018 schoolhouse year. This study demonstrates that using System 44 and READ 180 Universal to provide differentiated education in a mixed-model classroom is an effective method of increasing literacy for students struggling to achieve grade-level ELA proficiency.
-
College and Career Readiness and Success Center (CCRSC). (2013). Predictors of Postsecondary Success. Washington, DC: American Institute for Research.
-
U.S. Section of Education. National Section of Educational Progress (NAEP). (2017). The Nation's Report Bill of fare: 2017 Reading Assessment. Washington, DC: U.S. Section of Education.

Notation. One thousand = Mean; SD = Standard Divergence; n = sample size; 95% CI = 95% Confidence Interval; df = degrees of freedom; p = significance; SBA ELA = Smarter Balanced Assessment English/Language Arts & Literacy; FRPL = Free or Reduced-Cost Luncheon; EL = English language Learner.

Note. HMH RI = HMH Reading Inventory; Thou = Mean; SD = Standard Deviation; n = sample size; 95% CI = 95% Confidence Interval; df = degrees of liberty; p = significance; FRPL = Gratis or Reduced-Price Lunch; ELL = English Language Learner.

Note. M = Mean; SD = Standard Departure; n = sample size; 95% CI = 95% Confidence Interval; df = degrees of liberty; p = significance; SBA ELA = Smarter Balanced Assessment English language/Language Arts & Literacy; FRPL = Free or Reduced-Price Lunch; ELL = English Language Learner. Groups with fewer than 4 students were non included.

Notation. HMH RI = HMH Reading Inventory; Grand = Mean; SD = Standard Deviation; n = sample size; 95% CI = 95% Confidence Interval; df = degrees of freedom; p = significance; FRPL = Gratis or Reduced-Price Lunch; ELL = English language Language Learner. Groups with fewer than iv students were not included.
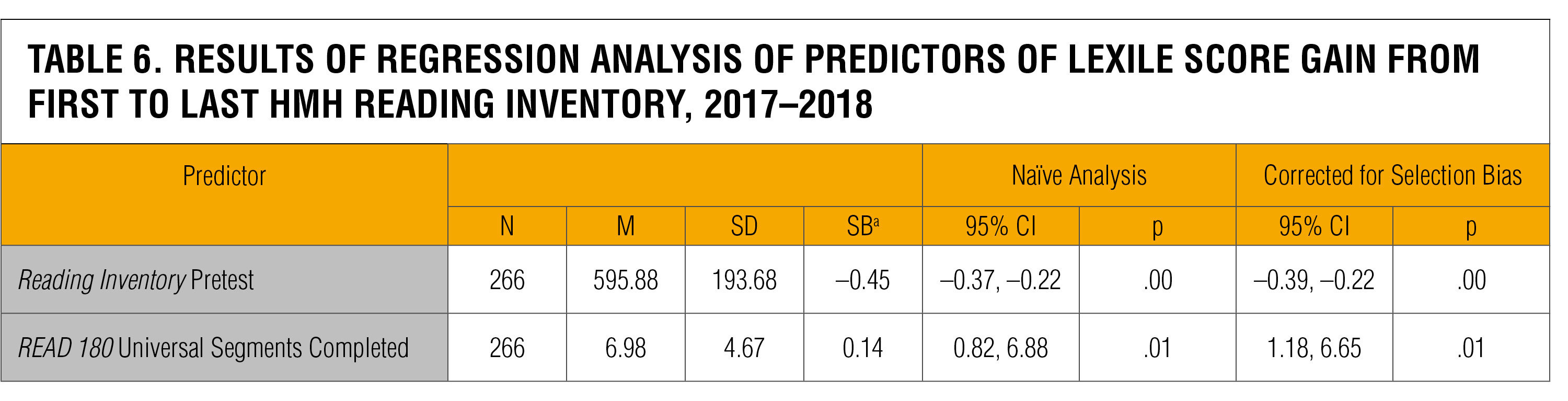
Annotation. N = sample size; M = Mean; SD = Standard Departure; SB = Standardized Beta; 95% CI = 95% Confidence Interval; p = significance; R180U = READ 180 Universal online application. aConcluding model too includes these covariates: school, historic period, race, gender, grade, English Language Learner classification, Students with Disabilities classification, and eligibility for the National Free or Reduced-Toll Luncheon plan.
kerstetterthippost.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.hmhco.com/research/read-180-universal-system-44-lincoln-unified-school-district
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Read 180 Universal Assessments for System 44"
Posting Komentar